
The UNIGE team wanted to find out whether the frontal and orbitofrontal regions of our brain activate in the same way when faced with human and simian vocalisations. Credit: Leonardo Ceravolo
A UNIGE team shows that the human brain is capable of identifying the vocalizations of certain primate species, if they are close to us and if the frequencies used are also close to our own.
Are we able to differentiate between the vocal emissions of certain primates? A team from the University of Geneva (UNIGE) asked volunteers to categorize the vocalizations of three species of great apes (Hominidae) and humans. During each exposure to these “onomatopoeia,” brain activity was measured.
Unlike previous studies, the scientists reveal that phylogenetic proximity—or kinship—is not the only factor influencing our ability to identify these sounds. Acoustic proximity—the type of frequencies emitted—is also a determining factor.
These results show how the human brain has evolved to process the vocal emissions of some of our closest cousins more efficiently. The study has been published in Cerebral Cortex Communications.
Our ability to process verbal language is not based solely on semantics, i.e., the meaning and combination of linguistic units. Other parameters come into play, such as prosody, which includes pauses, accentuation and intonation. Affective bursts—”Aaaah!” or “Oh!” for example—are also part of this, and we share these with our primate cousins. They contribute to the meaning and understanding of our vocal communications.
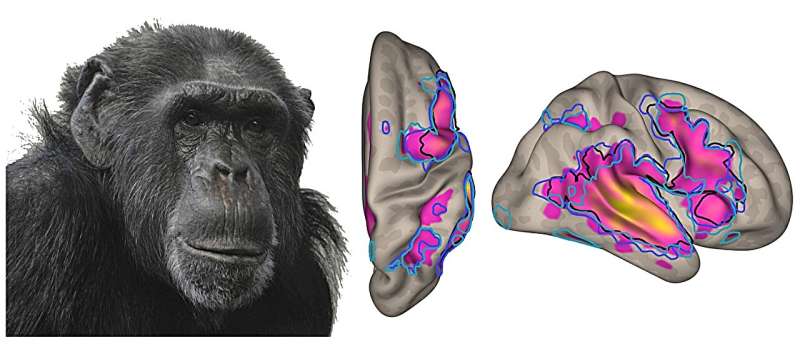
When such a vocal message is emitted, these sounds are processed by the frontal and orbitofrontal regions of our brain. The function of these two areas is, among other things, to integrate sensory and contextual information leading to a decision. Are they activated in the same way when we are exposed to the emotional vocalizations of our close cousins the chimpanzees, macaques and bonobos? Are we able to differentiate between them?
MRI scans with headphones on
A UNIGE team sought to find out by exposing a group of 25 volunteers to various human and simian vocalizations. “The participants were placed in an MRI scanner and were given headphones. After a short period of familiarization with the different types of vocalizations, each participant had to categorize them, i.e., identify to which species they belonged,” explains Leonardo Ceravolo, senior lecturer at the UNIGE’s Faculty of Psychology and Educational Sciences, and first author of the study.
These vocalizations were of the affiliative type, i.e., linked to a positive interaction, or of the agonistic type, i.e., linked to a threat or distress. The human vocalizations came from databases recorded by actors. The simian ones came from field recordings made as part of previous research. This study is the first of its kind to include bonobo vocalizations.
Bonobos, not so close cousins
The results show that for macaque and chimpanzee vocalizations, the frontal and orbitofrontal regions of the participants were activated in a similar way to human vocalizations.

